Technology


Technology support
In today's technology-driven world, computers can manage and analyse huge amounts of data. Half a century ago, such volumes of information depended on the ability of humans to input them.
Now that has changed - thanks to RFID technology.
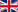
Tag any product, package or pallet with an RFID tag (a chip with an antenna) - and a suitably equipped computer can "see" and "interact" with that product, with virtually no human intervention.
How does it work?
- The reader uses an antenna to spread a radio frequency signal that reaches the RFID tag;
- At the same time, the reader receives a radio frequency response from the tag;
- The received analogue signal is translated into digital information which is processed by the control system.

RFID technology
RFID is dedicated to assets marking and tracking. It is based on radio frequency electromagnetic wave's use to read/write information into/from objects RFID tag. These operation are done using RFID readers antennas.
But RFID technology is not just a mechanism for computers to interact with inventory. The technology allows everyday objects to be given unique names (or numbers), and once an object has a name, the system can provide answers to interesting questions... When was it made? Where does it travel? Where is it placed? What is it for? When will it expire?
- Inventory management
- Efficient replenishment and receipt of goods
- Inventory movement tracking
- Effective quality control
- And many more...
Benefits:
- Written information can be changed;
- No need for direct line of sight for reading/writing;
- More durable;
- More information can be encoded inside a tag;
- Can read many tags at once;
- Fewer mistakes.
Drawbacks:
- Highly reliable on surroundings;
- Not fully standardized.
Our projects:
- More than 20 implementations of the asset inventory system MIVS.
- Many installations of stationary production capture gates, adapting to the client's needs and integrating with the client's ERP.
- Installations of RFID UHF label recording workstations (using both printers and stationary scanners).
- Modification of the IKEA ULL manager software by adding functions to RFID UHF label recording



Barcode technology
Barcode technology is similar to RFID in its use - assets marking and tracking, but differs in approach. Barcode technology is based on visual information (usually, parallel bars of certain thickness and at certain distances from each other). Barcode can be read using optical lasers.
Benefits:
- It is a standard for assets tracking throughout the world;
- Fewer mistakes;
- Data collection automatization;
- Easily implemented.
Drawbacks:
- Direct line of sight is necessary;
- Can read only one barcode ar a time;
- Less durable.

Customers
Our software
is already used by: